On July 19, 2024, a single software update from cybersecurity giant CrowdStrike caused unprecedented global IT chaos. Here’s what happened, why it matters, and how to recover if you’re affected by the CrowdStrike global outage.
- What is CrowdStrike?
- The Incident: What Happened?
- Impact: Who Was Affected?
- Root Cause Analysis
- Recovery Steps
- Lessons Learned
- FAQs
What is CrowdStrike?
CrowdStrike is a major technology company in the cybersecurity industry, known for its Falcon platform. Here’s what you need to know:
- Core Product: The CrowdStrike Falcon platform is designed to stop breaches via a unified set of cloud-delivered technologies.
- Market Share: According to Gartner, CrowdStrike accounts for 14% of the security software market by revenue.
- Key Features: Falcon provides endpoint protection, threat intelligence, and cyberattack response services.
The CrowdStrike Global Outage: What Happened?
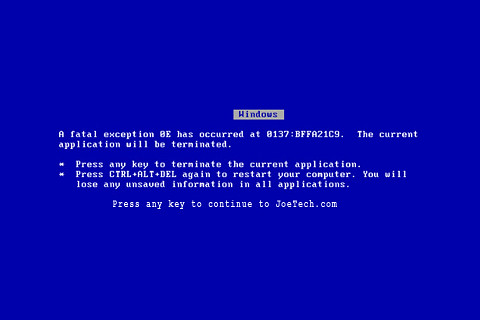
On July 19, 2024, CrowdStrike released a flawed Microsoft Windows software update that caused widespread system failures:
- The update was pushed to CrowdStrike’s Falcon monitoring product.
- Affected Windows computers entered a catastrophic reboot spiral, often displaying the “Blue Screen of Death.”
- Mac and Linux systems were not affected.
Impact: Who Was Affected?
The outage had far-reaching consequences across various sectors:
- Air Travel: Major airlines grounded flights, causing massive disruptions.
- Healthcare: Hospitals in multiple countries faced system outages.
- Banking: Many financial institutions experienced service interruptions.
- Media: Some TV stations, including Sky News in the UK, were unable to broadcast.
- Emergency Services: 911 systems in the US reported issues.
Root Cause Analysis
CrowdStrike’s CEO, George Kurtz, provided insights into what went wrong:
- The issue stemmed from a single configuration file pushed as an update to Falcon.
- The update was aimed at changing how Falcon inspects “named pipes” in Windows.
- This change was intended to catch a new method hackers were using for malware communication.
- The configuration update triggered a logic error, resulting in operating system crashes.
It’s important to note that this was not a cyberattack, but rather a technical glitch in the update process.
Recovery Steps
If your systems are affected, follow these steps to recover:
- Boot Windows into Safe Mode or Windows Recovery Environment (WRE).
- Navigate to C:\Windows\System32\drivers\CrowdStrike
- Locate and delete the file matching “C-00000291*.sys”
- Reboot normally.
For large organizations, this process may need to be repeated manually for each affected system, which could take considerable time.
Lessons Learned From The CrowdStrike Global Computer Outage

The CrowdStrike global outage incident highlights several important points:
- Interconnectedness of IT Systems: A single update can have cascading effects across global infrastructure.
- Importance of Testing: Even well-established companies can release faulty updates, emphasizing the need for rigorous testing.
- Backup and Recovery Plans: Organizations need robust plans to quickly recover from unexpected outages.
- Balancing Security and Stability: While frequent updates are crucial for security, they also introduce risks.
CrowdStrike FAQs
Q: Why is CrowdStrike so popular?
A: CrowdStrike’s popularity stems from its advanced cloud-native platform that provides comprehensive protection against various cyber threats.
Q: Does the US government use CrowdStrike?
A: Yes, CrowdStrike has been involved in cybersecurity investigations for the US government, including tracking North Korean hackers.
Q: What company owns CrowdStrike?
A: CrowdStrike is a publicly traded company (NASDAQ: CRWD) and is not owned by any single entity or company.
Q: How long did the outage last?
A: The full duration varied, but many systems required manual intervention, which extended the recovery time for some organizations to days.
Q: Could this happen again?
A: While unlikely, the incident has prompted discussions about changing the model of pushing updates without IT intervention to prevent similar future occurrences.











 Marlon Brando’s Unorthodox Acting Techniques Led to Iconic Performance in ‘The Godfather’
Marlon Brando’s Unorthodox Acting Techniques Led to Iconic Performance in ‘The Godfather’
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.